Treating abdominal aortic aneurysm
Your treatment options will depend on the size and severity of the aneurysm, its growth rate, and whether you are experiencing symptoms. CT or MRI imaging can be used by your doctor to monitor the size and growth rate of your aneurysm.
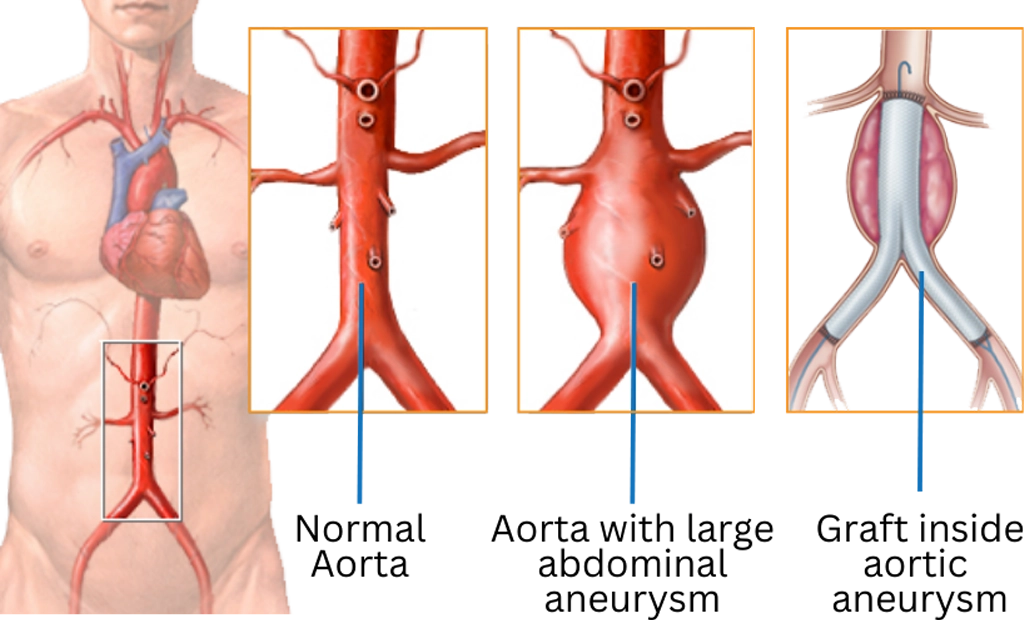
If the aneurysm is not life-threatening, it may be treated with medication and/or lifestyle changes, such as losing weight and quitting smoking. Diabetics can better control blood sugar which is a risk factor for developing AAAs. If these methods fail, and the aneurysm continues to grow to over 5.5 centimeters, there are two main interventions:
Surgical repair is an open surgery to replace the damaged part of the aorta with a special graft. It requires general anesthesia and a hospital stay of up to two weeks. While effective, not all patients are candidates for surgery, as they may have other health conditions.
Endovascular repair is a minimally invasive procedure performed inside the body, using tiny catheters that are guided by imaging through the blood vessels and to the aorta. Once the aorta is reached, a special stent or graft is placed and expanded so that it attaches to the wall of the aorta.
Recent clinical studies show endovascular aneurysm repair has lower perioperative mortality, less operative blood loss, and lower transfusion requirements compared with patients undergoing open surgery. Because patients can return home the following day, the length of hospital stay is dramatically reduced. If the aneurysm has ruptured (“dissection”), there is also an endovascular repair procedure for those unable or unwilling to have open surgery.
The interventional radiologists at IntelliRad perform endovascular aortic aneurysm repair at leading hospitals and health centers throughout south Florida. We are among the most experienced doctors in the region in performing this procedure.